Vroom 1964 Expectancy Theory Pdf Download
Vroom Expectancy Theory Definition
Vroom's expectancy theory. Dept of Engineering. Victor Vroom suggested that the relationship between people's behavior at work and their goals was not as simple. Vroom's expectancy theory. Dept of Engineering. Victor Vroom suggested that the relationship between people's behavior at work and their goals was not as simple.
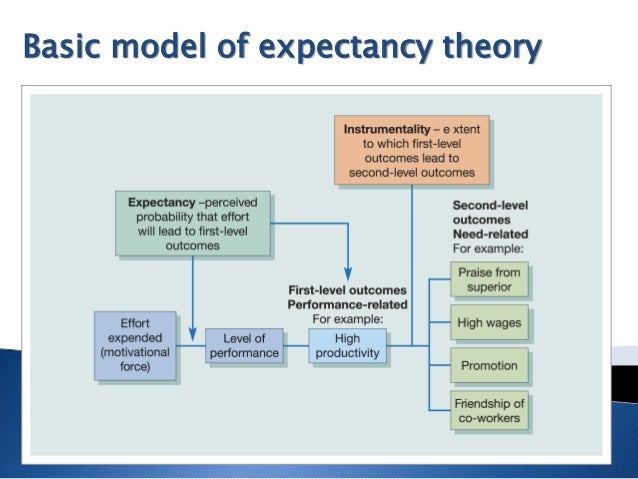
• • • Vroom expectancy motivation theory Vroom expectancy motivation theory Whereas Maslow and Herzberg look at the relationship between internal needs and the resulting effort expended to fulfil them, Vroom's expectancy theory separates effort (which arises from motivation), performance, and outcomes. Vroom's expectancy theory assumes that behavior results from conscious choices among alternatives whose purpose it is to maximize pleasure and to minimize pain. Vroom realized that an employee's performance is based on individual factors such as personality, skills, knowledge, experience and abilities. He stated that effort, performance and motivation are linked in a person's motivation. He uses the variables Expectancy, Instrumentality and Valence to account for this.
Expectancy is the belief that increased effort will lead to increased performance i.e. If I work harder then this will be better. This is affected by such things as: • Having the right resources available (e.g. Raw materials, time) • Having the right skills to do the job • Having the necessary support to get the job done (e.g. Supervisor support, or correct information on the job) Instrumentality is the belief that if you perform well that a valued outcome will be received.
The degree to which a first level outcome will lead to the second level outcome. If I do a good job, there is something in it for me. This is affected by such things as: • Clear understanding of the relationship between performance and outcomes – e.g. The rules of the reward 'game' • Trust in the people who will take the decisions on who gets what outcome • Transparency of the process that decides who gets what outcome Valence is the importance that the individual places upon the expected outcome. For the valence to be positive, the person must prefer attaining the outcome to not attaining it.
For example, if someone is mainly motivated by money, he or she might not value offers of additional time off. The three elements are important behind choosing one element over another because they are clearly defined: effort-performance expectancy (E>P expectancy) and performance-outcome expectancy (P>O expectancy). E>P expectancy: our assessment of the probability that our efforts will lead to the required performance level. P>O expectancy: our assessment of the probability that our successful performance will lead to certain outcomes. Crucially, Vroom's expectancy theory works on perceptions – so even if an employer thinks they have provided everything appropriate for motivation, and even if this works with most people in that organisation, it doesn't mean that someone won't perceive that it doesn't work for them. At first glance expectancy theory would seem most applicable to a traditional-attitude work situation where how motivated the employee is depends on whether they want the reward on offer for doing a good job and whether they believe more effort will lead to that reward.
Outlook incluye controladores de vista previa de datos adjuntos que funcionan. Para desactivar un controlador de vista previa de datos. 1 febrero 2017 a las. Controlador de vista previa outlook 2017. En Outlook 2016 al recibir adjuntos de Excel y querer hacer una. Vista previa del mismo sin el mensaje de error del controlador de vista previa. En Outlook 20016 no puedo visualizar en vista previa los archivos de Excel. Me marca que el controlador no esta instalado cuando yo lo veo habilitado en la tabla de controladores activos de Outlook. Describe un problema que se produce cuando se intenta obtener una vista previa de un libro de Excel que se. Salga de Outlook. Controlador de vista previa de.
Victor Vroom Expectancy Theory 1964
However, it could equally apply to any situation where someone does something because they expect a certain outcome. For example, I recycle paper because I think it's important to conserve resources and take a stand on environmental issues (valence); I think that the more effort I put into recycling the more paper I will recycle (expectancy); and I think that the more paper I recycle then less resources will be used (instrumentality) Thus, Vroom's expectancy theory of motivation is not about self-interest in rewards but about the associations people make towards expected outcomes and the contribution they feel they can make towards those outcomes. Download our FREE ebook 'A summary of motivation theories' to get an overview and brief practical analysis all the theories in one handy document. Fill in your coordinates and we’ll send it to you right now.
Name *: E-mail adress *: Type verification numbers *. Adobe acrobat crack serial number. We hate spam too. We'll only send you what you asked for. View our and.
Vroom Expectancy Theory Pdf
Expectancy theory in comparison to the other motivation theories There is a useful link between Vroom's expectancy theory and Adam's Equity theory of motivation: namely that people will also compare outcomes for themselves with others. Equity theory suggests that people will alter the level of effort they put in to make it fair compared to others according to their perceptions. So if we got the same raise this year, but I think you put in a lot less effort, this theory suggests that I would scale back the effort I put in.